Flat valgus foot: Surgical procedure, after-care and costs
- Who qualifies for surgery?
- What happens before surgery?
- How is the surgery performed at Gelenk-Klinik?
- Which doctors specialise flat valgus foot surgery?
- What success rate can I expect?
- What type of anaesthesia is used during surgery?
- After-care, rehabilitation and aids following flat valgus foot surgery
- What do I need to keep in mind following flat valgus foot surgery?
- Should I expect pain after flat valgus foot surgery?
- What will my stay be like at Gelenk-Klinik?
- What is the cost of flat valgus foot surgery?
- How can international patients schedule surgery?
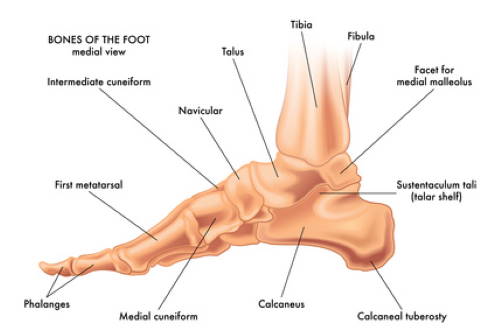 View of the bones of the longitudinal arch of the foot: Flat valgus foot arises due to a rolled-out calcaneus and drop of the arch in the talonavicular joint (joint between the ankle and navicular bone). The hindfoot deformity resulting from a flat valgus foot can also affect the upper ankle joint due to deformity of the talus (ankle). © rob3000, Fotolia
View of the bones of the longitudinal arch of the foot: Flat valgus foot arises due to a rolled-out calcaneus and drop of the arch in the talonavicular joint (joint between the ankle and navicular bone). The hindfoot deformity resulting from a flat valgus foot can also affect the upper ankle joint due to deformity of the talus (ankle). © rob3000, Fotolia
Flat valgus foot is a deformity of the foot where the calcaneus is rolled out. At the same time, the arch of the foot drops at the inside. The flat valgus foot is most commonly caused by being overweight, wearing the wrong footwear and lack of exercise. Even damage to the posterior tibial tendon (tendon of the back tibial muscle) can promote the deformity. In addition, women from middle age and beyond are three times as likely to develop flat valgus foot than men. Typical symptoms of the flat valgus foot are swelling of the inside edge of the foot and the inside ankle, particularly whilst bearing weight. In the early stages, insoles and consistent foot exercises help strengthen the ligaments in the foot. If all conservative treatment options have been exhausted, there are various surgical procedures. The exact extent of the surgery is determined by the physician together with the patient following a medical and diagnostic examination. Possible surgical procedures include, for example, reshaping the bone (osteotomy) or transplanting the posterior tibial tendon.
Who qualifies for surgery?
Flat valgus foot surgery is determined by the stage of the condition. Surgery should be recommended only following thorough deliberation. Due to the dynamic situation in the arch of the foot, training and strengthening the muscle can be quite effective.
However, if unbearable pain is present for quite some time and the person’s quality of life has been affected, surgery can be an option. Chronic tendinitis or even ruptures of the posterior tibial tendon require surgery. Surgery is also indicated for contracted (stiffened) deformities of the hindfoot along with arthrosis of the ankle joints.
What happens before surgery?
Prior to surgery, the physician will conduct detailed medical diagnostics. One criterion for diagnosing flat valgus foot is the “too many toes” sign. Flattening of the arch of the foot causes the front of the foot to point outward. If the physician now looks at the foot from the heel, so from the back, almost all toes can be seen past the side of the outside of the ankle due to the change in the longitudinal axis of the foot. In patients without foot deformity, the toes point forward. An X-ray, taken whilst standing, shows the deformity of the bone and can confirm the physician’s suspected diagnosis.
Another sign is the “single limb heel rise” sign. It suggests a problem with the posterior tibial tendon. For this test, the physician examines the position of the foot from behind whilst the patient is standing. If the axis of the ankle shows a medial (inward) deviation, the posterior tibial tendon is probably injured. An MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) scan further helps the orthopaedist to assess the condition of the posterior tibial tendon. In addition, a podometric examination is helpful in analysing the pressure points of the foot whilst standing and running.
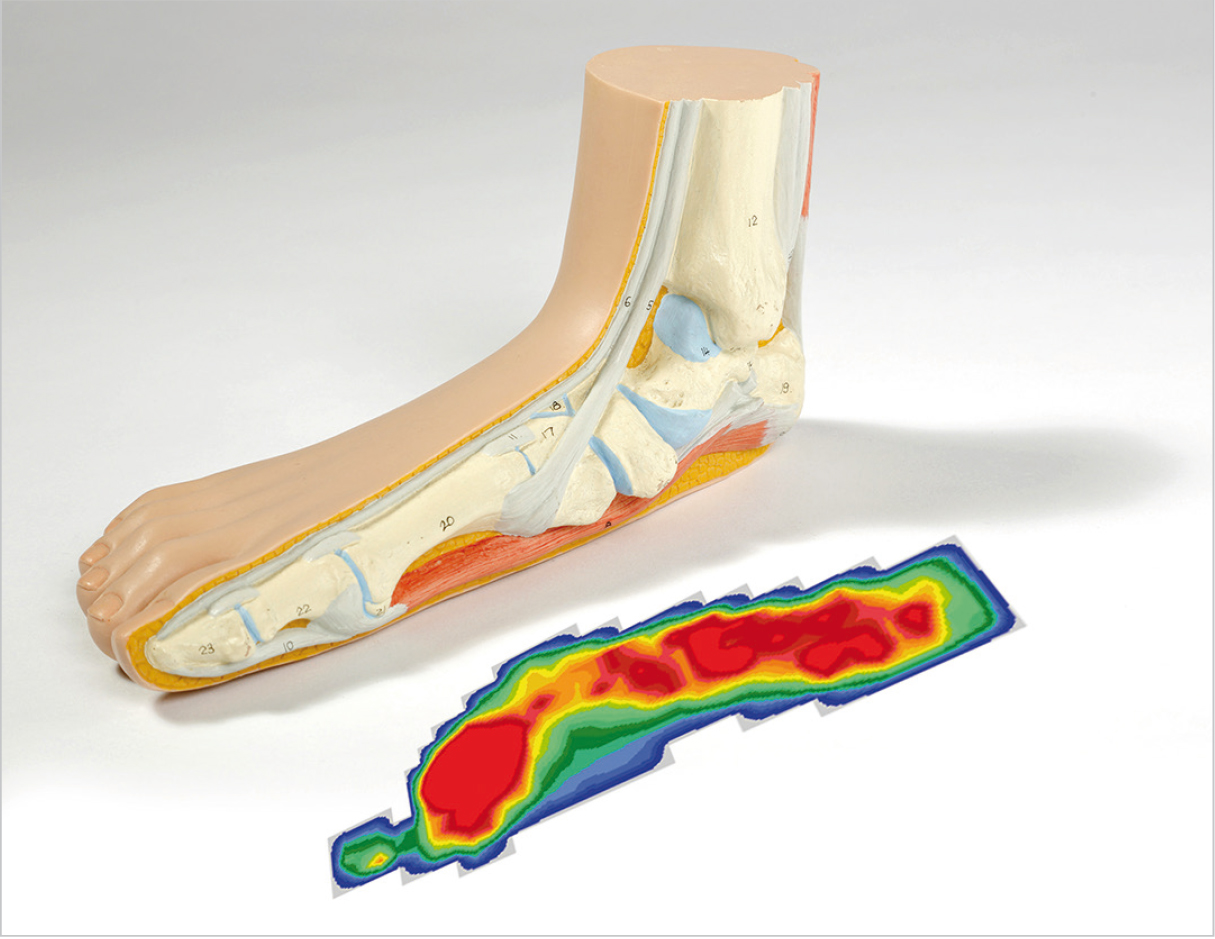 Deformity of the arch can be determined using a footprint test (podometrics): The imprint (red area) is more spread out than in a healthy foot. With a normal arch only the heel and ball of the foot bear weight. So, with flat valgus foot, the longitudinal arch has collapsed.
Deformity of the arch can be determined using a footprint test (podometrics): The imprint (red area) is more spread out than in a healthy foot. With a normal arch only the heel and ball of the foot bear weight. So, with flat valgus foot, the longitudinal arch has collapsed.
How is flat valgus foot surgery performed at Gelenk-Klinik?
Flat valgus foot surgery for inflamed posterior tibial tendon
The surgical technique for flat valgus foot is based on the underlying cause. For mild inflammation of the posterior tibial tendon, removing the inflamed connective tissue surrounding the tendon (synovectomy) will typically suffice. If necessary, the posterior tibial tendon can be shortened slightly and sutured in place (“tightened").
If the degeneration of the tendon is already advanced or in the case of a rupture, it can be replaced with an autologous tendon graft. A prerequisite for the success of this transplantation is a functioning tibialis posterior muscle. The graft is also harvested from the foot. The nearby long-toe flexor tendon (tendon of the flexor digitorum longus muscle) is excellent for this purpose. The patient will experience minimal limitations from moving the tendon. Only the toe movement will be slightly reduced. However, the lesser muscular traction from moving the tendon will often result in the transplant requiring additional supporting measures related to the bones.
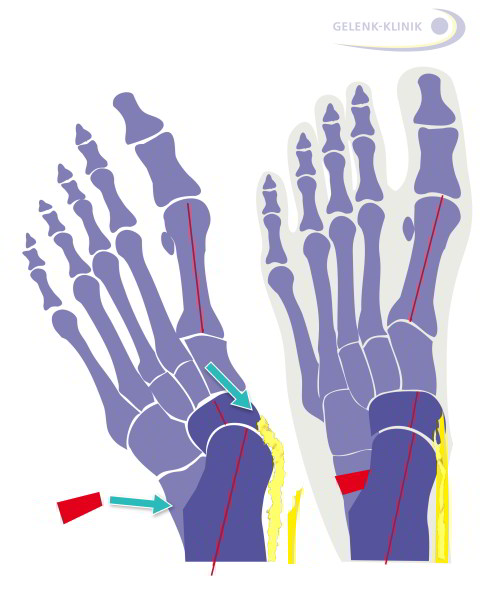 Sketch of the flat valgus foot with the weakened posterior tibial tendon (yellow). This tendon is involved in the normal arch shape. Sketch on right: flat valgus foot following surgery. The tighter posterior tibial tendon and the autologous (body’s own) bone implant raise the arch. © joint-surgeon
Sketch of the flat valgus foot with the weakened posterior tibial tendon (yellow). This tendon is involved in the normal arch shape. Sketch on right: flat valgus foot following surgery. The tighter posterior tibial tendon and the autologous (body’s own) bone implant raise the arch. © joint-surgeon
Osteotomy (bone reshaping) with calcaneus deformity
If the cause of a flat valgus foot is a deformed calcaneus, a medial displacement osteotomy (MDO) can be performed to move the bone. Shifting the calcaneus inward will also shift the direction the Achilles tendon is pulling in. This will straighten the foot as a whole.
Another technique for correcting a flat valgus foot is inserting a bone wedge in the calcaneus. This wedge is commonly harvested from the iliac crest bone (Hintermann system or Evans osteotomy).
Arthrodesis (immobilisation) of the talus
If the incorrect biomechanical strain on the feet over long periods has resulted in severe, painful arthrosis of the ankles, possibly along with tendon degeneration, immobilisation (arthrodesis) is often the only option to restore the pain-free function of the ankles. In some cases, triple arthrodesis is even indicated. This immobilises all flexible joints of the talus: toward the back/bottom to the calcaneus, toward the front to the navicular bone, as well as the joint between the calcaneus and the cuboid bone.
Which doctor specialises in flat valgus foot surgery?
Here at Gelenk-Klinik we believe a close relationship between the physician and their patient is important. Meaning, you will be in the care of your treating foot specialist from your initial appointment until after the flat valgus foot surgery. This physician is also responsible for your aftercare. So, you will have one contact person who will be assigned to you throughout your stay at Gelenk-Klinik. As a certified Centre for Foot and Ankle Surgery (ZFS), Gelenk-Klinik is committed to maximum standards and experience in the area of flat valgus foot surgeries. Our foot and ankle surgery experts are Dr Thomas Schneider and Dr Martin Rinio.
What success rate can I expect?
With a proper indication, surgical treatment of flat valgus foot is very successful and long-lasting. Depending on the type of procedure (e.g., bone reshaping), however, it may take relatively long before full weight-bearing of the foot is achieved. We, therefore, consider these procedures very carefully. Posterior tibial tendon surgery is very promising if the flat valgus foot deformity has not yet caused arthrosis of the ankles. So, if the deformity is still soft and orthopaedic insoles alone do not bring about long-term improvement, surgery or reconstruction of the posterior tibial tendon can stabilise the longitudinal arch of the foot again.
What type of anaesthesia is used for the surgery?
We typically perform flat valgus foot surgery under general anaesthesia. However, we also offer spinal anaesthesia to avoid the risks of general anaesthesia. In this case, the anaesthetist injects the anaesthetic into the vertebral canal of the lumbar spine. In this case, the patient is fully conscious during surgery. Our anaesthetists are very experienced in both methods and choose the option best for you and your circumstances during a mutual pre-operation discussion.
After-care, rehabilitation and aids following flat valgus foot surgery
During the first few days following surgery the operated foot will be wrapped in an elastic compression dressing. After this, you will receive a special VACOped boot which allows partial weight bearing up to 20 kg. You will further receive forearm crutches to reduce strain on the foot. Thrombosis prophylaxis (e.g. Heparin/Enoxaparin) is vital during this time. You should further use compression socks until full weight bearing has been restored.
What do I need to keep in mind following flat valgus foot surgery?
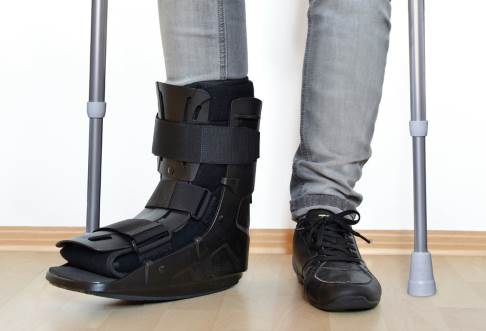 You will receive a rigid VACOped boot during the first 6 weeks. © sunnychicka, Fotolia
You will receive a rigid VACOped boot during the first 6 weeks. © sunnychicka, Fotolia
You should elevate your foot as much as possible following surgery to rest it. A rigid VACOped boot help rest your foot during the first 6 weeks. You will receive antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent infection. X-rays are necessary after the 4th and 8th week to monitor the position of the foot. Once the wound is fully healed you can resume seated activity. Full weight bearing of the foot will take 6 weeks. If your job requires a lot of walking or standing, you should wait 8 weeks before returning to work. Physiotherapy and exercises prevent muscular atrophy and help restore the physiological gait pattern.
- Inpatient treatment: 3 days
- Optimal local stay: 10–14 days
- Earliest return flight: 12 days after surgery
- Recommended return flight: 14 days after surgery
- Showering permitted: 12 days after surgery
- Recommended time off work: 6 weeks (varies by job)
- Recommended removal of sutures: 10 days after surgery
- Time before you can drive again: 6 weeks
- Low-impact exercise: 3 to 6 months after surgery
- Normal exercise: 9 months after surgery
Should I expect pain after flat valgus foot surgery?
Any procedure causes pain. We always strive to minimise pain as much as possible. The respective anaesthetist will often use a so-called nerve block before the surgery, numbing the affected foot for approx. 30 hours. This already manages the greatest wave of pain, which can then be easily treated with regular medication. Our goal is for you to experience as little pain as possible.
What will my stay be like at Gelenk-Klinik?
 Single-occupancy room at the orthopaedic clinic in Gundelfingen, Germany
Single-occupancy room at the orthopaedic clinic in Gundelfingen, Germany
During your inpatient stay at Gelenk-Klinik you will have a single-occupancy room. The room has a bathroom with a shower and WC. All rooms include towels, a bathrobe and slippers. They further include a mini-bar and a safe. All rooms also have a television. You only need to bring your personal medication, comfortable clothes and sleepwear. After surgery, you will receive 24-hour care by experienced nursing staff and experienced physiotherapists. The inpatient stay is typically 3 days after the flat valgus foot surgery. Your family members can stay at a hotel within walking distance. We will gladly take care of making the reservations.
What is the cost of flat valgus foot surgery?
In addition to the cost of surgery you will also need to plan for additional costs for diagnosis, physician’s appointments and aids (e.g. VACOped boot). These amount to between €1 500 and € 2000. If you plan to have outpatient physiotherapy in Germany after surgery, we will gladly schedule the appointments with the physiotherapists and obtain an estimate of costs.
You will find information about the cost of hotel lodging and any follow-up treatment at the rehabilitation clinic on the websites of the respective providers.
How can international patients schedule surgery?
We will first need recent MRI images and X-rays of the foot to assess the position of the bone and the state of the posterior tibial tendon. After sending these to us using the contact form on our website, we will send you patient information including proposed treatment and a binding estimate of costs within 1–2 days.
Gelenk-Klinik offers quick appointments for international patients to correspond with your preferred travel itinerary. We will gladly help you apply for a visa once we have received the down payment specified in the cost estimate. If the visa is denied, we will refund the full down payment.
We try to minimise the time between the preliminary examination and the surgery for our international patients to avoid additional travel. During your inpatient and outpatient stay our multi-lingual (English, Russian, Spanish, Portuguese) case management team will be there to assist you. We can also provide an interpreter (e.g. Arabic) at any time, at the patient’s expense. We will gladly assist you with organising transportation and lodging and provide recreational tips for your family members.