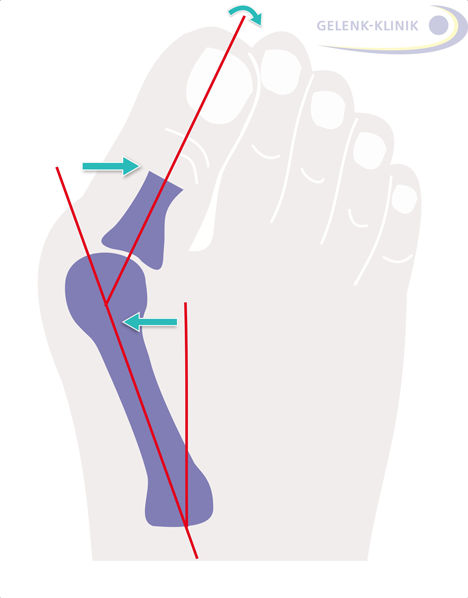
 The operation of the Hallux valgus (bunion) corrects the deformity of the big toe, which tilts toward the outside of the foot. © joint-surgeon
The operation of the Hallux valgus (bunion) corrects the deformity of the big toe, which tilts toward the outside of the foot. © joint-surgeon
Hallux valgus (usually called a bunion) is a common deformity of the big toe that is predominantly seen in female patients. The big toe noticeably tilts toward the outside of the foot, displacing the smaller toes. The deformity is not pretty. It is of particular concern to women whose feet no longer fit into shoes. In advanced stages, the deformity puts increasing strain on the base joint of the big toe. In the long term, the adjacent toes will develop claw or hammer toes. The base of the big toe will grow painful exostoses (outgrowths) or develop extremely painful bursitis, only worsening the problems wearing shoes. The protruding part of the ball of the foot becomes inflamed and may swell up. The strain on the base joint of the big toe may even cause painful osteoarthritis in the big toe (hallux rigidus). Often specialists speak of “Cinderella Foot Surgery” to focus on the cosmetic point of view of foot procedure. But improving the function, relieving chronic pain and treating deformities of the foot are equally important.
The specialists at our certified centre for foot and ankle surgery are experts in the gentle treatment of this deformity of the big toe. They typically use gentle, minimally invasive procedures which often leave no visible scars on the foot. This speeds up healing and rehabilitation and prevents complications following bunion surgery.
The more severe the bunion, the more complex the surgery will be and the longer the after-care period. It is therefore prudent to see a specialist early and learn about surgical options for correcting bunions.
The goal of treatment is for our patients to regain mobility as quickly as possible and experience permanent medical and cosmetic improvement of their bunion with minimal scarring.